Halftone Options
The detailed options of the vector halftone effect are edited in the Halftone Style modal view. The Halftone Style view can be accessed from the Halftone panel, or by using the Halftone Options command from the Styles - Halftone menu.
The halftone options can be saved and reused as styles or presets. The Styles field opens a list of previously created halftone styles and presets. The Create Style and Create Preset commands of this list are used to create new styles or presets from the current options.the current options.
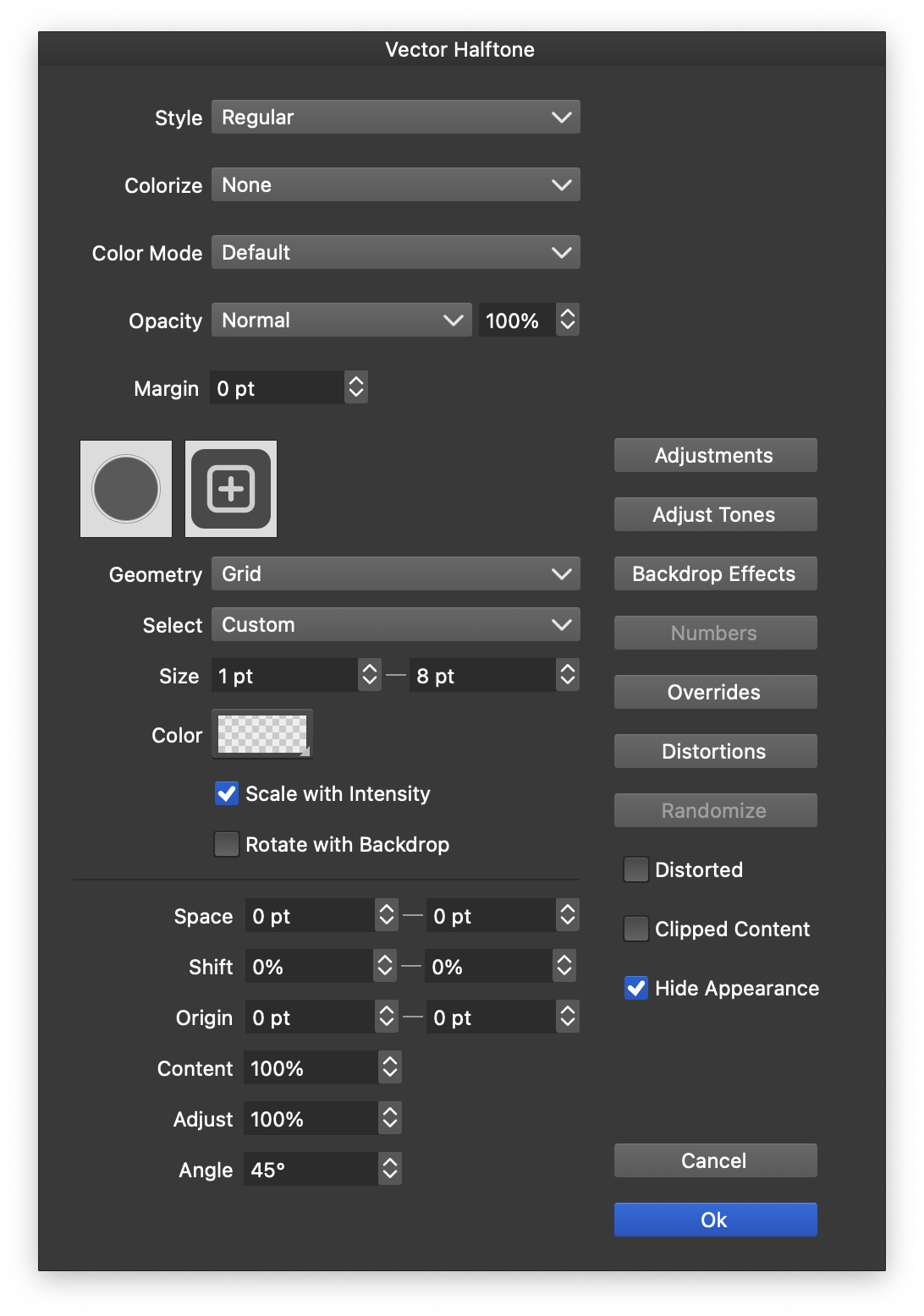
The halftone style view.
Managing the Shapes
The Regular and Stippling halftone types can use multiple shapes to simulate the backdrop intensity. When multiple shapes are used, the shape of a dot can be selected by various intensity schemes, including the backdrop intensity.
- The Halftone Style modal view provides a list shapes with their previews, and a possibility to manage this list.
- To add a new shape, click on the “plus” icon and select a shape for the menu.
- Any previously saved shape style or preset can be used as long as it is a closed shape. Objects with the Shape role will also show up in this list.
- To remove a shape, select the shape and press the Delete key.
- To change a shape, double click on the shape and select another one from the menu.
Halftone Options
The halftone style view provides access to the following common halftone options:
- Style - Select the halftone type, and also create and reuse halftone presets and styles.
- Colorize - Select a colorization scheme for the halftone dots or strokes. The Backdrop Content colorization scheme is used to sample colors from the backdrop of the halftone.
- Color Mode - Select the halftone color mode. The color mode can be used to create halftones based on a specific color channel.
- Opacity - Select the halftone opacity and blending mode options.
- Margin - Set the amount of expansion to the halftone area when generating halftone dots or shapes. This area expansion is used when distorting halftone dot positions with shape effects and extra dots are needed due to the distortion movements.
- The halftone shape list for Regular and Stippling halftone types is shown in a horizontal grid list.
The above options are common regardless of the halftone category.
VectorStyler supports the following halftone categories:
- Regular halftones are similar to geometry types in repeaters. In this case the halftone dots are arranged in some form of regular (or random) positions. The options for regular halftones are similar to the repeater geometry options.
- Stippling halftones use randomly positioned halftone dots with varying density to simulate color tones.
- Width halftones use variable stroke widths on user selected shapes to simulate color tones.
- Overlay halftones use variable widths shape overlays (as in the Overlay shape effect), to simulate color tones.
- Content halftones use an arbitrary group of objects and resize each object according to the corresponding backdrop location tone.
The halftone style selected in the Style field determines the halftone category, and each category uses a different set of options to control the halftone effect.
Regular Halftones
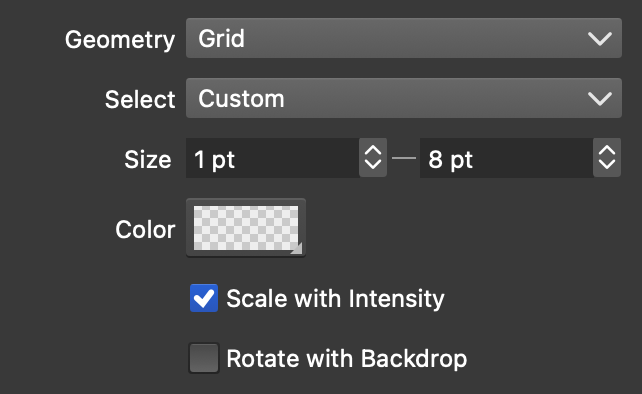
Regular halftone options.
Regular halftones use repeater geometries to create regular or random dot positions using some geometry type. Typically, the dots are placed at regular intervals, and the backdrop tone is simulated by creating shapes with varying sizes at the dot locations.
The following options are available for regular halftones:
- Geometry - Select or edit a repeater geometry used to create positions for regular halftones. More details on this can be found in the repeater Geometries page.
- Select - Choose a shape selection mode when multiple shapes are used. For single shapes, the Voronoi selection mode can be used to create Voronoi halftones (see below).
- Size - Set the minimum and maximum size for the halftone dot shape. The actual shape size will be between these sizes in function of the backdrop intensity.
- Color - Set the color used for the halftone dot shapes. The color can also be sampled from the backdrop using the Colorize field of the halftone options.
- Scale with Intensity - Check to scale the halftone shape using the selected intensity (backdrop is the default). This option is selected by default, as the regular halftones use dot shape sizes to approximate tone. This option can be disabled to keep shape sizes fixed, when shapes are colorized using the backdrop color.
- Rotate with Backdrop - Rotate the halftone dot shape using the backdrop image gradient direction.
- Each geometry type has a specific set of options, similar to the repeater geometry options. More details on this can be found in the repeater Geometries page.
Stippling Halftones
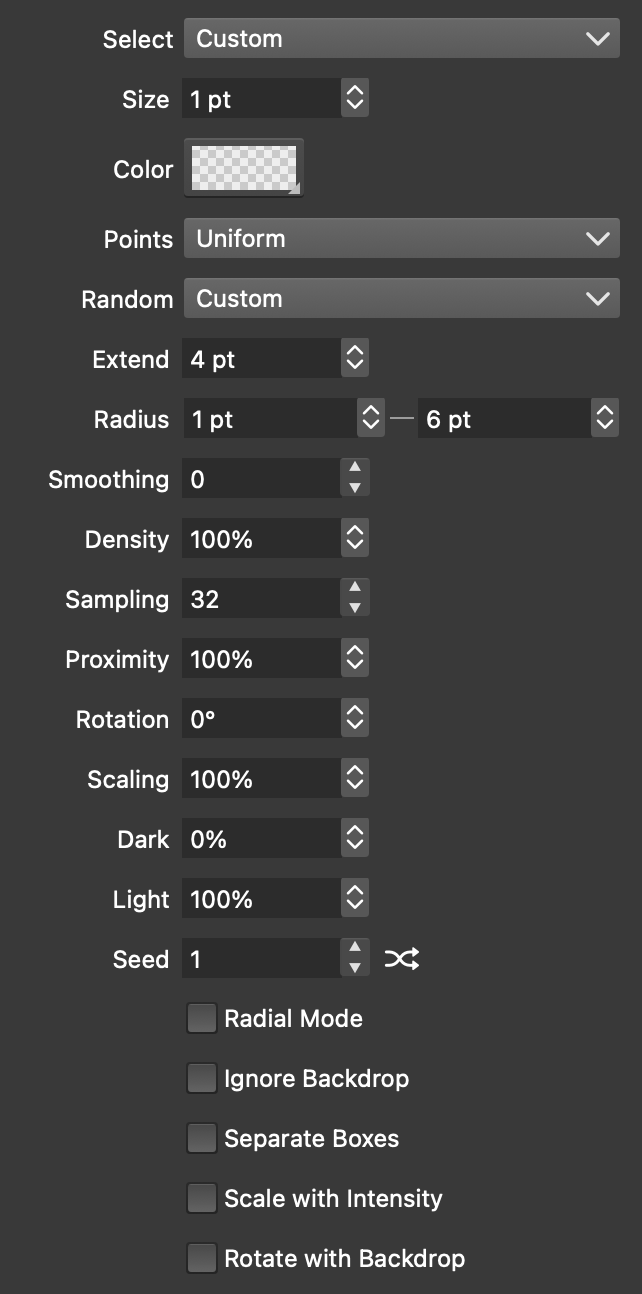
Stippling halftone options.
Stippling halftones place halftone dots randomly and use the dot density to simulate the backdrop color intensity. Typically the dots are of the same color and size, and their placement density depends on the color intensity.
The stippling halftone type can be used with the Voronoi shape selection mode to create randomized Voronoi halftones.
The following options are available for stippling halftones:
- Select - Choose a shape selection mode when multiple shapes are used. For single shapes, the Voronoi selection mode can be used to create Voronoi halftones (see below).
- Size - Set the halftone dot size. This will be the shape size place at a halftone dot, and will not affect the density.
- Color - Set the color used for the halftone dot shapes. The color can also be sampled from the backdrop using the Colorize field of the halftone options.
- Points - Select a random point location generator scheme.
- Random - Select a random number generator scheme. Different random number generator can be used to obtain different stippling point distributions
- Extend - Set an additional region extension amount to generate extra stippling locations when distortions are used.
- Radius - Set the minimum and maximum distance between stippling points. This sets the density variation limits of the stippling effect.
- Smoothing - Set the number of smoothing steps for the random point locations.
- Density - Set the point density factor, controlling the amount of random point locations.
- Sampling - Set the point sampling count.
- Proximity - Set the point proximity factor allowing for more or less point density.
- Rotation - Set the rotation of the stippling pattern.
- Scaling - Additional scaling factor for the shape sizes.
- Dark - Set the intensity level for dark tones (maximum point density).
- Light - Set the intensity level for light tones (minimum point density).
- Seed - Set the randomization seed number.
- Radial Mode - Check to generate random points in polar coordinates.
- Ignore Backdrop - Check to ignore the backdrop for point density. When checked the point density will be uniform (with random point locations). This option can be used to simulate color tones by dot size, or when the dot colors are sampled from the backdrop.
- Separate Boxes - Generate separate stippling location for Glyphs in a text shape.
- Scale with Intensity - Scale the stippling dot sizes using the backdrop intensity.
- Rotate with Backdrop - Rotate the stippling dot shape using the backdrop image gradient direction.
Voronoi Halftones
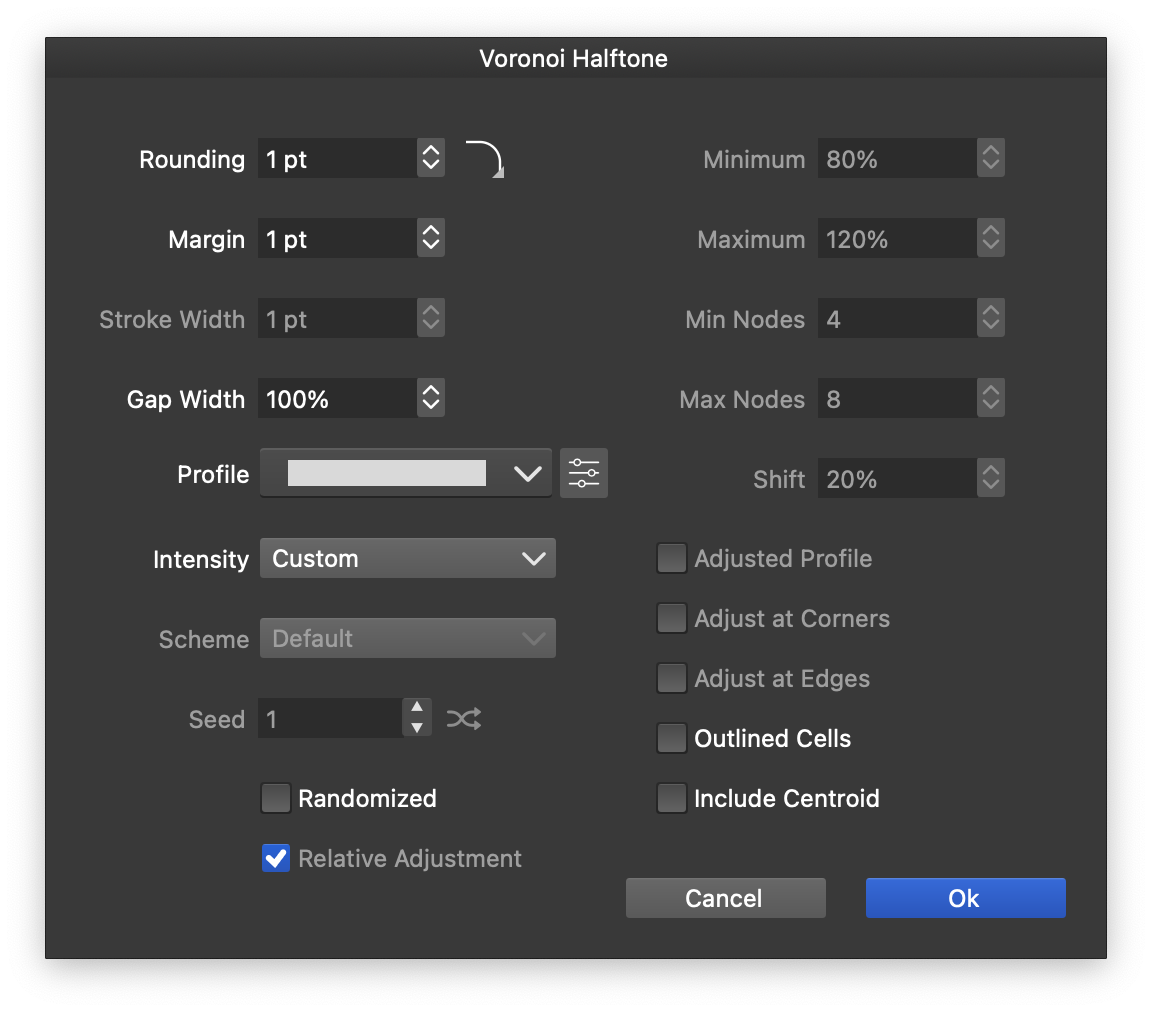
Voronoi halftone options.
Voronoi halftones can be created using the Stippling (or Regular) halftone modes, by setting the shape Select mode to Voronoi. The Voronoi halftone options can be edited using the Edit Shape Mode option in the Select drop down menu.
When the Voronoi halftone shape mode is used, the halftone shapes are generated by creating a Voronoi diagram of the halftone points from the Stippling halftone type. This will result in a set of packed shapes filling the halftone region.
The following options are available for Voronoi halftone shapes:
- Rounding: Set the rounding of the corners of the Voronoi cell shapes.
- Margin: Set the spacing between the Voronoi cells. The spacing is achieved by offsetting the cell shapes.
- Stroke Width: Set the stroke width used on show the Voronoi cell shapes. This option is available if the Outlined Cells option is checked.
- Gap Width: Set the average width of the variable gap relative to the margin. Variable width gaps can be created between Voronoi cells using the Profile option.
- Profile: Set the variable width profile for the gap between Voronoi cells.
- Intensity: Set the variable width adjustment intensity mode.
- Scheme: Set the randomization scheme used to adjust Voronoi cell gaps.
- Seed: Set the randomization seed.
- Randomized: Check to use randomization for the Voronoi cell gaps.
- Relative Adjustment: Check to adjust the randomized profile relative to its current values.
- Minimum: Set the minimum cell gap when variable width gap is used.
- Maximum: Set the maximum cell gap when variable width gap is used.
- Maximum: Set the maximum cell gap when variable width gap is used.
- Min Nodes and Max Nodes: Set the minimum and maximum number of nodes in the sampled width profile.
- Shift: Set the relative shift of the width profile, along the Voronoi cell shape.
- Adjusted Profile: Check to adjust the current width profile when randomizing.
- Adjust at Corners: Check to adjust the width profile at Voronoi cell corners.
- Adjust at Edges: Check to adjust the width profile at Voronoi cell edges.
- Outlined Cells: Check to show the Voronoi cell shapes in outlined (not filled) mode.
- Include Centroid: Check to show the halftone shape (selected for the Stippling or Regular halftones) at the centroid of the Voronoi cell.
Width Halftones
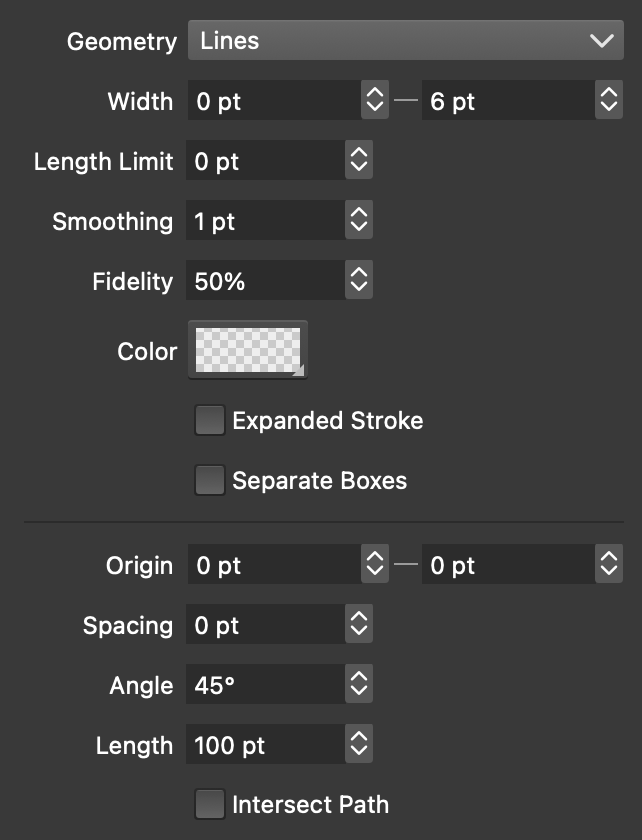
Width halftone options.
Width halftones use variable stroke widths on a space filling shape to simulate backdrop intensities. The basic width halftone is a regularly spaces set of lines with variable stroke widths.
The width halftones can be customized with user defined shapes
The following options are available for width halftones:
- Geometry - Select the geometry used to generate shapes for the width halftone. The Curves geometry requires a complete shape filling shape suitable to cover the halftone region. These shapes can be created and customized by the user.
- Width - Set the minimum and maximum halftone stroke width. The backdrop color tones are simulated using varying stroke widths between these values.
- Length Limit - Set the maximum length of a path with variable stroke width. Limiting the path lengths in the halftone results in better variable width profile generation based on the backdrop tone. But, very small limits may result in more computation.
- Smoothing - Set the smoothing factor of the variable width profile.
- Fidelity - Set the fidelity of the variable width profile.
- Color - Set the color used for the halftone stroke shapes.
- Expanded Stroke - Check to generate expanded outlines for the width halftone. This option can be used in combination with halftone shape distortion for various effects.
- Separate Boxes - Check to generate separate halftone paths for each Glyph in a text shape.
- Depending on the Geometry of the width halftone, the halftone shape options are shown next. The halftone shape is used to create a space filling shape that covers the area of the halftone region.
- Angle - Set the halftone rotation angle. This will rotate the shape on which the variable width strokes are applied.
- Intersect Path - Check to intersect the halftone shape with the object shape, creating a set of path sections that are inside the object shape.
The Geometry selection determines the halftone shape used to create variable width strokes. These geometry types are also available for the Overlay halftone mode. The following halftone shapes are available:
- Lines: A set of parallel lines at a distance defined by the maximum stroke width and an additional Spacing amount.
- Curves: A user defined space filling curve. This can be any group of objects containing shapes that would cover the area of the halftone region. This geometry mode allows the creation of custom halftone shapes.
- Shapes: A set of closed shapes repeated in a concentric form. The default shape is a circle resulting in a circular width halftone. Any closed shape defined by the user can be selected here.
- Stripes: A set of open shapes repeated in a parallel form. The default shape is a line resulting in a linear grid width halftone. Any open shape defined by the user can be selected here.
- Waves and ZigZag: Uses the corresponding shape type options to generate waving or zigzag shaped grid for the halftone.
- Spiral, Swirling, Polygonal Spiral: Uses the corresponding shape type options to generate spiral, swirling or polygonal spiral space filling shapes for the halftone.
Overlay Halftones
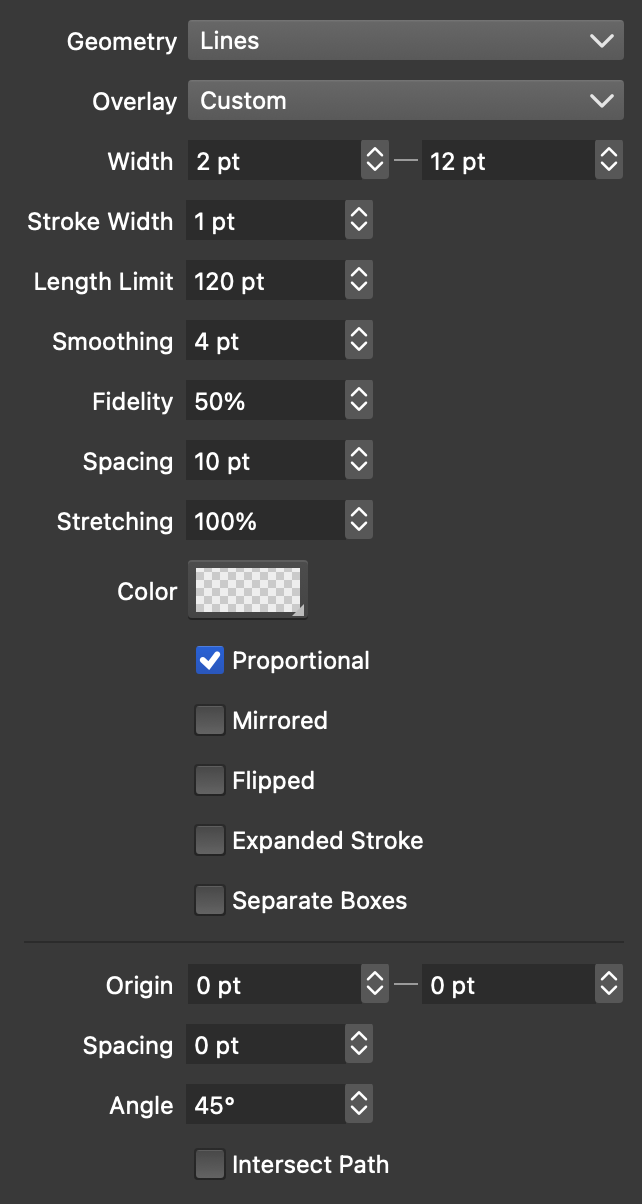
Overlay halftone options.
Overlay halftones use variable width shape overlay effects on a space filling shape to simulate backdrop intensities. The basic overlay halftone is a regularly spaces set of lines using a circle shape as the variable width overlay.
The overlay halftones can be customized with user defined shape filling shapes
The following options are available for overlay halftones:
- Geometry - Select the geometry used to generate shapes for the overlay halftone. The Curves geometry requires a complete shape filling shape suitable to cover the halftone region. These shapes can be created and customized by the user.
- Overlay - Select the shape used in the overlay effect.
- Width - Set the minimum and maximum width of the overlay effects. The backdrop color tones are simulated using varying stroke widths between these values.
- Stroke Width - Set the uniform stroke width used to render the shapes resulting from the overlay effect.
- Length Limit - Set the maximum length of a path used in the overlay effect. Limiting the path lengths in the halftone results in better variable width profile generation based on the backdrop tone. But, very small limits may result in more computation.
- Smoothing - Set the smoothing factor of the variable width profile used in the overlay effect.
- Fidelity - Set the fidelity of the variable width profile used in the overlay effect.
- Spacing - Set the amount of spacing used in the overlay effect. The spacing will affect the density of the overlay shapes.
- Stretching - Set the amount of stretching of the overlay shapes.
- Color - Set the color used for the halftone stroke shapes.
- Proportional - Check to generate proportionally scaled overlay shapes.
- Mirrored - Check to use mirroring when repeating overlay shapes.
- Flipped - Check to use flip overlay shapes vertically when repeating.
- Expanded Stroke - Check to generate expanded outlines for the width halftone. This option can be used in combination with halftone shape distortion for various effects.
- Separate Boxes - Check to generate separate halftone paths for each Glyph in a text shape.
- Depending on the Geometry of the width halftone, the halftone shape options are shown next. The halftone shape is used to create a space filling shape that covers the area of the halftone region.
- Angle - Set the halftone rotation angle. This will rotate the shape on which the variable width strokes are applied.
- Intersect Path - Check to intersect the halftone shape with the object shape, creating a set of path sections that are inside the object shape.
The Geometry selection determines the halftone shape used in the overlay shape effect. These geometry types are the same as the ones available for the Width halftone mode.
Content Halftones

Content halftone options.
The Content halftone type uses shapes from a group of user defined objects or symbols to generate the halftone effect. This enables the user to setup any custom collection of shapes, covering the halftone region and use this as a halftone. The backdrop tone is simulated by scaling the corresponding object over the backdrop location.
- Shapes - Select the symbol or group of objects with the Symbol object role, to be used as the halftone. The selected group will be scaled to cover the halftone region.
- Origin - Set the center offset of the halftone shapes to the region.
- Size - Set the minimum and maximum scaling amount for the content of the group.
- Scale - Set the additional scaling applied to the halftone content group, after it is scaled to the region.
- Scale with Intensity - Check to scale the content group objects using the backdrop intensity.
- Rotate with Backdrop - Check to rotate the content group objects using the backdrop image gradient direction.
